Population interactions in the boreal forest
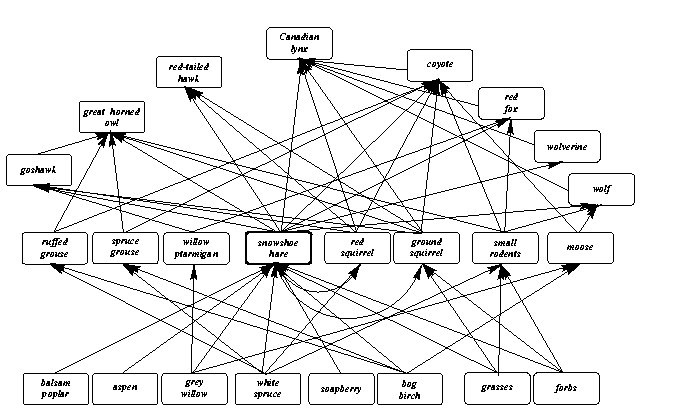
Click to see a larger version of the food web of the
boreal forest community (after Stenseth et al., 1998).
![]() he above diagram
depicts part of the food web of the Canadian boreal forest (after Stenseth
et al., 1998). Essentially there are three trophic levels. During the summer,
various herbs and grasses support a community of herbivores dominated (65%-80%
total herbivore biomass) by the snowshoe hare (Lepus americanus).
During the winter, some of the herbivores hibernate, while others, including
the hare, remain active. The latter species depends on woody browse and
is itself a principal source of nutrition for many species. The top trophic
level is comprised of mammalian and avian predators which differ both with
regard to mobility and their dependence on the hare.
he above diagram
depicts part of the food web of the Canadian boreal forest (after Stenseth
et al., 1998). Essentially there are three trophic levels. During the summer,
various herbs and grasses support a community of herbivores dominated (65%-80%
total herbivore biomass) by the snowshoe hare (Lepus americanus).
During the winter, some of the herbivores hibernate, while others, including
the hare, remain active. The latter species depends on woody browse and
is itself a principal source of nutrition for many species. The top trophic
level is comprised of mammalian and avian predators which differ both with
regard to mobility and their dependence on the hare.
M & B Home | Previous | Top | Next